The Earth is a terrestrial planet, which means it is primarily composed of rock and metal. It is the third planet from the Sun in our solar system.
Size: With a diameter of about 12,742 kilometers, the Earth is the fifth-largest planet in the solar system. Its equatorial circumference is approximately 40,075 kilometers.
Mass: The mass of the Earth is about 5.97237×10²⁴ kilograms, which is large enough to generate a gravitational force that can hold the atmosphere and all objects on the planet’s surface.
The Earth’s atmosphere is mainly composed of nitrogen (about 78%) and oxygen (about 21%), with trace amounts of other gases such as carbon dioxide and argon. This atmosphere plays a crucial role in protecting life on Earth by blocking harmful solar radiation and regulating the temperature.
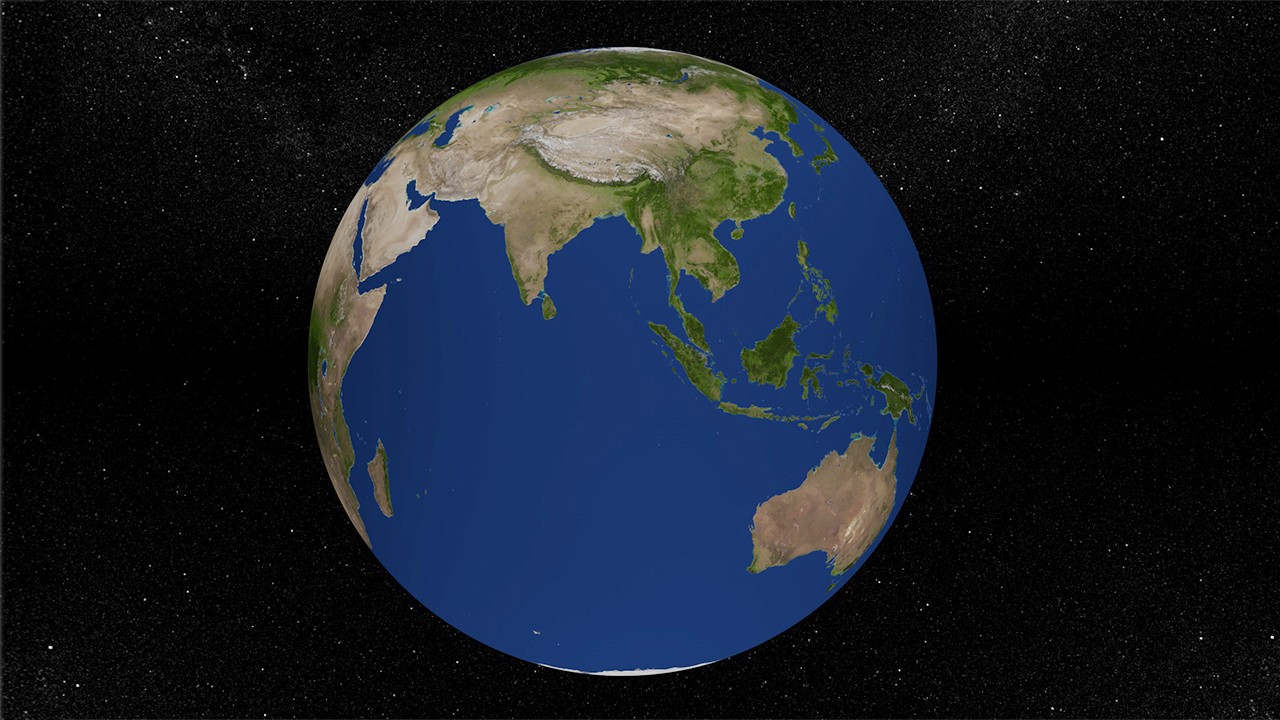
Hydrosphere: The Earth is often called the “blue planet” because about 71% of its surface is covered by water. The hydrosphere includes oceans, seas, lakes, rivers, and groundwater. The vast oceans not only have a significant impact on the climate but also provide a habitat for a large number of organisms.
Lithosphere: The Earth’s lithosphere is composed of the crust and the upper part of the mantle. It is divided into several large tectonic plates that are constantly moving. This movement leads to geological phenomena such as earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and the formation of mountains.
Leave a Reply